Post updated June 11, 2020
More than 10 percent of all Information Industry jobs were lost by May, according to preliminary labor department statistics.
There are six Information industries which employed about 2.8 million people in February before stay home orders began. Jobs were lost in all of the six industries.
None of the Information industries gained jobs in May as some stay home orders were relaxed. There were job gains in other sectors such as Construction, Manufacturing, Financial activities, and Retail.
The Motion Picture and Sound Recording industry was hardest hit among Information industries -- more than half of its 456,000 jobs were gone by May. Five other industries suffered job losses ranging from more than 8 percent in Broadcasting to 0.37 percent in Other Information Services. Other Information includes search engines and digital publishers and broadcasters.
This post describes changes in employment for all six Information industries from May 2019-May 2020. I also report employment in selected occupations as of May, 2019.
The first chart shows aggregate employment in all six industries.
The chart (above) shows monthly changes in Information sector employment. Data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics is seasonally adjusted to remove the influence of predictable influences such as seasonal changes or holiday hiring. This provides a more accurate estimate of changes caused by factors like the pandemic.
April and May employment statistics are preliminary and subject to revision.
The six Information industries employed more than 2.8 million people from May 2019-Feb. 2020. The industries had lost an estimated 316,000 jobs by May, a decline of 10.9 percent.
Information is part of the private, nonfarm business sector which employed 129.7 million people in February 2020. The sector had lost an estimated 21 million jobs by April. Some industries in this sector added jobs in May. But the entire sector was still down 17.9 million jobs since February, a decline of 13.8 percent.
Subsequent charts report employment in each of the six industries.
The second chart (above) shows Other Information Services, which includes search engines, internet-only publishing and broadcasting, and web sites that store and provide information.
Employment increased by 19,000 jobs from May 2019-Feb. 2020. Other Information employed 354,400 people in February.
The industry added jobs in March. However, Other Information had lost an estimated 1,300 jobs by May, a decrease of 0.37 percent.
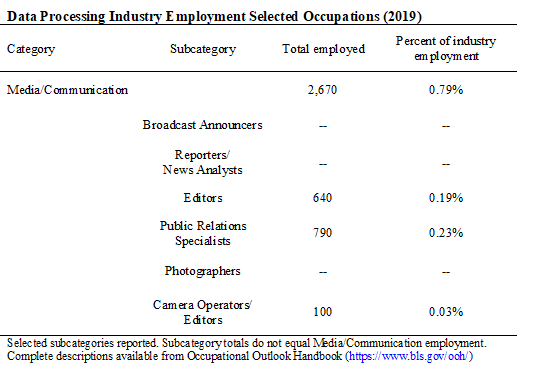
The table (below) reports 2019 employment in selected occupations. This is the most recent available data.
Employment in selected occupations is a rough indicator of the relative importance of specific jobs. However, these jobs may not be evenly distributed across the entire industry.
About 6 percent of Other Information employees were in Media occupations in 2019. Half were editors, and less than 2 percent were reporters
Editors may be employed at digital firms that do and do not produce original content. Reporters, however, are concentrated at a small number of digital news publications.
Computer jobs (not shown) are also reported for each industry to provide a comparison. Computer jobs and technology can be used to produce, distribute, and sell media and other information products.
Computer jobs were 24.2 percent of employment in Other Information in 2019.
The third chart (above) shows Telecommunications, which includes distribution and services for telephones, cable and satellite broadcasting, and internet access.
Employment in Telecommunications decreased by about 16,000 jobs from May 2019-Feb. 2020. The industry employed about 700,000 people in February.
An estimated 12,800 jobs were lost by May, a decrease of 1.8 percent.
Media occupations were less than 1 percent of this industry in 2019. The industry does not produce original media content, so this is expected.
Computer jobs (not shown) accounted for 16.3 percent of employment in Telecommunications.
The fourth chart (above) shows Publishing, which includes newspapers, magazines, books, directories and software publishing.
Employment in Publishing increased by about 12,000 people from May 2019-Feb. 2020. The industry had 770,000 jobs in February.
An estimated 28,000 jobs were lost by May, a decrease of 3.6 percent.
Media workers were about 10 percent of all Publishing jobs in 2019. Editors were almost 6 percent of industry jobs, probably because editors were employed by magazines and book publishers in addition to newspapers. Reporters were 2.5 percent of the industry, jobs that were concentrated in newspapers.
Computer occupations (not shown) accounted for 31 percent of Publishing jobs in 2019. Computer jobs may be more widely distributed than media jobs in this industry.
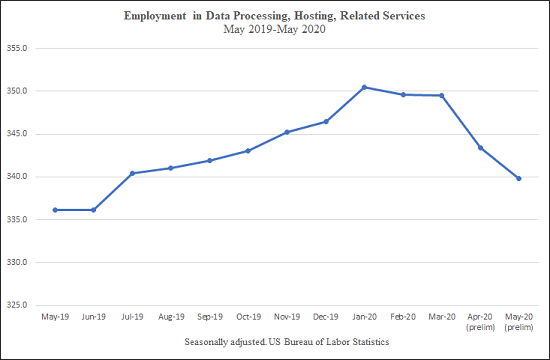
The fifth chart (above) shows Data Processing, which includes hosting and providing data processing services.
Employment increased by about 13,000 jobs from May 2019-Feb. 2020. Data Processing employed about 349,000 people in February.
An estimated 9,800 jobs were lost by May, a decrease of 2.8 percent.
Less than 1 percent of jobs were in Media occupations in 2019. This is another industry that does not produce media content.
Computer jobs (not shown) accounted for 40 percent of Data Processing employment. This is expected because the industry is defined by computing.
The sixth chart (above) shows Broadcasting, an industry that creates, acquires and distributes content via radio, television, cable and other subscription services.
Broadcasting employment decreased by about 4,000 jobs from May 2019-Feb. 2020. The industry employed 263,300 people in February.
Broadcasting lost an estimated 23,000 jobs by May, a decrease of 8.7 percent.
About 21 percent of Broadcasting jobs were in Media occupations in 2019. Broadcast Announcers and Disc Jockeys were 9 percent of all jobs, probably because they were employed by television and radio stations.
Reporters were about 6 percent of all jobs and camera operators and editors were 3.6 percent of jobs, possibly because these were concentrated at television stations.
Computer jobs (not shown) accounted for just 4.8 percent of Broadcasting employment in 2019.
The seventh chart (above) shows Motion Picture and Sound Recording, which includes the production and distribution of motion pictures and sound recordings.
Employment was steady at about 450,000 people until February 2020.
The industry lost an estimated 240,900 jobs by May, or about 52.7 percent.
This unusually large decline may result from collaboration between many people in the same place when making a movie or a recording. Covid-19 makes physical proximity dangerous.
Only 3.5 percent of Motion Picture and Sound jobs were in Media occupations in 2019.
Camera operators and editors were listed as a major category, accounting for another 3.5 percent of all jobs. There were more than twice as many camera operators and editors, 27,560, as in Broadcasting with 9,690.
Computer jobs (not shown) were just 1.5 percent of employment in Motion Pictures and Sound.
Comments
Employment changes during the pandemic are probably influenced by whether employees can keep working, how much demand and revenue still exists for the industry's products, and long-term employment trends.
The pandemic is having the smallest effect on Other Information Services. This may be because employees can work from home. This may also result from increased demand for internet services when millions of people were ordered to stay home as much as possible. Online advertising is generally cheaper than ads in Broadcasting or Publishing, so increased demand also means the industry can continue selling ads.
Smaller adverse effects on employment also appear in other industries where technology may allow people to work from home, such as Data Processing and Telecommunications. However, both industries employ thousands of sales agents who may be unable to work. Telecommunications demand for cell phone services may also be affected if customers are losing their jobs and incomes.
Publishing jobs losses are increasing. Some employees may be able to work from home such as book and magazine editors and computer employees. Employment in Publishing as a whole was also increasing before the pandemic.
However, some Publishing sectors such as newspapers had decreasing employment before the pandemic. The initial pandemic response from some large newspaper companies included cutting hours worked and using furloughs to avoid layoffs. But these are interim measures that might not be enough to stave off layoffs.
The largest adverse effects appear to be industries where workers must gather in the same location to produce news and entertainment products. Broadcasting is also losing advertising revenue because large advertisers are reducing spending as consumers buy fewer advertised products.
Most dramatically, Motion Picture and Sound Recording jobs vanished as the production of movies and television programs shut down.